Bearing Manufacturer & Supplier
Specialize in ball bearings, roller bearings, thrust bearings, thin section bearings etc.
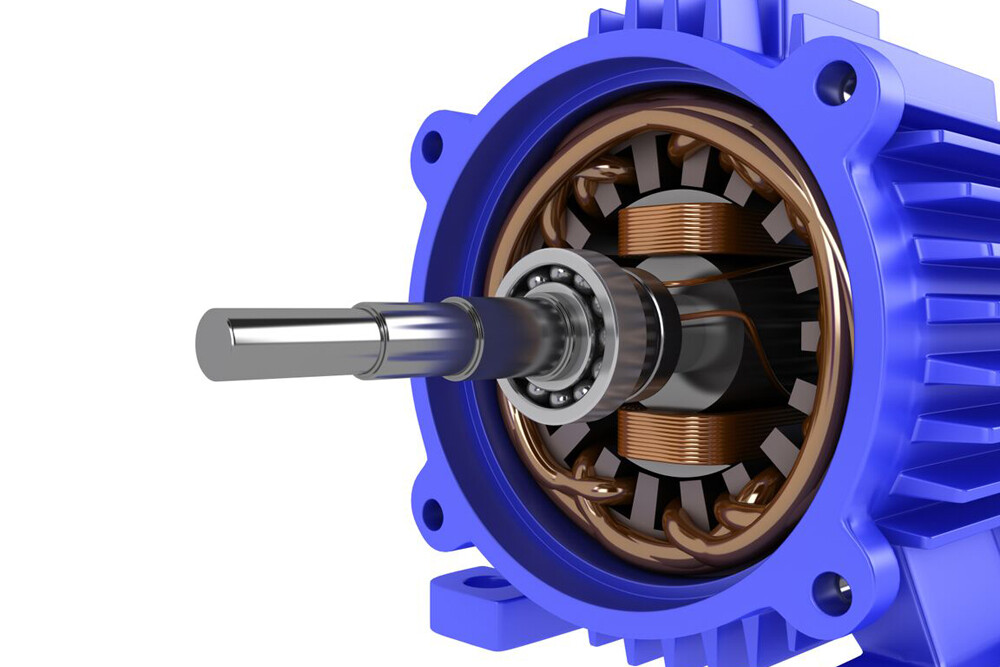
The Ultimate Guide to Motor Bearings
Electric motor bearings, also known as EMQ bearings, are a type of bearing used to support electric motors. Rotating motor bearings transmit power between various components or rotate a shaft to provide power. Bearings should be able to operate at low and high speeds while minimizing friction losses. At the same time, the bearings must be economical and require as little maintenance as possible. To help you purchase suitable EMQ bearings, this blog covers everything you need to know about electric motor bearings.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat are motor bearings?
Motor bearings support and position the rotor and are designed to ensure that the motor transfers load from the shaft to other components smoothly and efficiently. That is, it can withstand the high speeds and loads imposed by electric motors, making it suitable for high-performance applications while ensuring a long service life. These bearings are available in a variety of sizes and designs to meet the specific needs of different electric motors. Electric motor bearings need to withstand a variety of forces, including radial and thrust loads, as well as vibration and shock. To withstand these forces, bearings must be carefully designed and manufactured. The most commonly used material for electric motor bearings is chromium steel, but other materials such as ceramic or plastic can be used in some applications.

Motor bearing standards
Many manufacturers have developed EMQ bearing standards that apply to their manufacturing. For example, JEM bearings manufactured by SKF are manufactured with a J-steel cage and are designated “EM” to indicate motor mass. Motor quality means each manufacturer has noise specifications, usually C-3 internal clearance and grease specified for the motor. SKF’s noise specification designation is QE6 and indicates that GJN specifies Mobil Polyrex EM, a high quality polyurea thickened grease. But unlike ABEC bearing standards, EMQ bearing standards are not unified. Bearing manufacturers such as SKF, NTN and FAG may all have their own EMQ bearings, possibly specifying different types of grease, radial clearance and noise specifications.

Motor Bearing Type
The main performance characteristics of motor bearings are high load capacity, high-speed operation, high-precision positioning, low noise, etc. The design and use of electric motors vary among different industries, so there are many types of bearings used to support the motors. They are widely used in electronic appliances, large factory machinery, electric vehicles, railways, wind turbines, etc. Different types of bearings are used in different scenarios to power them. Selection of motor bearing type depends on the specific design, load conditions, operating environment and other factors. Electric motor engineers carefully consider these factors to ensure optimal performance, longevity and efficiency for a given application. Roller bearings are usually used for heavy loads, while ball bearings are chosen for lighter loads.

Deep Groove Ball Bearings
Ideal for applications requiring high rotational speeds and moderate axial and radial loads. They are typically used in small and medium-sized motor non-belt and direct-coupled applications, typically in motors up to 150 horsepower. The most common application for this type of motor bearing is in AC motors.

Self-aligning ball bearings
Self-aligning ball bearings can accommodate misalignment between the shaft and housing, typically 3 degrees, making them suitable for motors where shaft misalignment may occur due to assembly or operation. They help reduce friction and wear caused by misalignment.

Sealed Bearings
These are specially designed for environments prone to contamination. Sealed bearings are common in small motors and can significantly limit the ingress of contaminants. Unlike open bearings, these bearings are not relubricable, so the total bearing life is limited and require immediate replacement should problems occur.

Angular Contact Bearings
Angular contact ball bearings are capable of supporting both radial and axial loads in high-speed rotation applications. This is particularly useful in applications where loads or precise positioning is required. For example, electric motors in machine tools and robots often use angular contact ball bearings. They are available in single or double row configurations and can be used in pairs.

Ceramic hybrid bearings
Ceramic hybrid bearings are becoming and popular in recent years. They are composed of steel rings and ceramic balls, so they are called "hybrid bearings". Silicon nitride rolling elements provide excellent electrical insulation and improved heat dissipation. Hybrid bearings require no lubrication, have smaller rotating mass, require less maintenance, and have a longer service life, thus reducing subsequent maintenance costs.

Shielded Bearings
The shield is made of metal and is fixed to the outer ring on both sides of the bearing. Shielded bearings are specifically designed to protect electric motors from dust, dirt and other debris. Metal shielding prevents contaminants from entering and damaging sensitive components, ultimately protecting and extending the life of your bearings.

Spherical roller bearings
Spherical roller bearings are designed for motors that carry heavy radial and axial loads and are commonly used in large industrial applications where motors may be severely misaligned or heavily loaded, such as those in conveyor belts and crushers.

Needle Roller Bearings
Needle roller bearings feature cylindrical rollers with a high aspect ratio. They are used in compact motor designs and applications where space is limited and high radial load capabilities are required, such as power tools and automotive starter motors.

Thrust bearings
Thrust bearings are used in electric motors that bear large axial loads. This axial (thrust) load is the force along the axis that components such as motor shafts are able to withstand. Thrust bearings are critical for electric motors where axial loads are present in high-speed and heavy-duty applications, such as automotive transmissions.

Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Cylindrical roller bearings operate efficiently at medium and high speeds, are designed for belt or gear driven motors and are well suited for radial loads. Generally they are not used to handle axial loads. Cylindrical bearings are commonly used as non-locating bearings on the drive side of large and medium-sized electric motors for motor applications of at least 150 HP.

Tapered Roller Bearings
Tapered roller bearings are separable bearings and can be easily installed on the motor. Tapered roller bearings have a large load-bearing capacity and can operate stably under heavy loads and impact loads. This makes them ideal for heavy-duty motors. Examples include electric motors used in car hubs or industrial gearboxes. Tapered roller bearings have different structural forms such as single row, double row and four rows.

Electrically Insulated
Electrically insulated bearings use a special spraying process to spray a high-quality coating on the outer surface of the bearing. The coating has strong bonding force with the matrix and has good insulation performance. It can avoid the electroerosive effect of induced current on the bearing and prevent the current from affecting the grease and rolling elements. , damage caused by the raceway and improve the service life of the bearing.
Factors causing damage to motor bearings
Motor bearing failure is the most common, because the bearing is the most easily worn part of the motor and is the heaviest-loaded part. Generally, when the motor is running, the bearing temperature exceeds 95 degrees and is easily damaged. Some of the most common causes of motor bearing failure include:
lubricating. Lubrication is an important cause of motor bearing damage. Bearings require a certain amount of lubrication when running. If the lubricating oil is insufficient or of poor quality, it will cause excessive wear and even burnout of the bearings. Wear occurs when two dry and dissimilar surfaces rub against each other, leading to corrosion. In addition, the wrong lubrication method or the use of a lubrication method that is not suitable for the bearing will also affect the bearing life.
Environment: Motor bearing damage is highly related to environmental factors. For example, using a motor in a high temperature, harsh humidity or dirty environment will cause the inner and outer rings of the bearing to be deformed or damaged. Contaminants such as water, sand, dirt, and chemicals can cause a variety of problems with bearing assemblies. For example, they can erode/corrode bearing surfaces or degrade lubricants, all of which can lead to premature failure.
Dislocation. Shaft and Bearing Seat In addition, use under high vibration conditions can also cause early damage to the motor bearings. Misalignment can cause excessive vibration and uneven load distribution, leading to material fatigue and cracks in bearing components leading to failure.
Installation is incorrect. Bearing failure can be caused by incorrect installation and setup. The most common installation errors include imbalance, incorrect installation, misalignment, or excessive shaft runout.
Electrical damage. The flow of electrical current through bearings can cause electrical corrosion or arcing, leading to lubricant degradation, pitting damage to rolling elements and raceways, and premature bearing failure.
Motor bearing lubrication
Incorrect lubrication is one of the main causes of motor bearing failure. It is very important to maintain bearings with regular lubrication, so how often should they be lubricated? Motor manufacturers and bearing manufacturers will have a specific recommended lubrication schedule. Lubrication intervals will depend on the motor load, operating hours and ambient temperature. Common intervals are monthly, quarterly, or yearly. Often, the bearing manufacturer may also specify how much grease to use. If your motor is running every day, you will need to lubricate it frequently than if you have a motor that is only running a few times a week. Over-oiling can cause as many problems as under-oiling. Too little oil can cause increased friction and heat, leading to lubrication failure and premature bearing wear. Too much grease can cause pressure to build up inside the bearing, which can lead to increased friction and heat.

Conclusion
This blog covers all aspects related to electric motor bearings. None When selecting bearings, you should consider design and specifications. One of the factors you must always keep in mind is which type of bearing is best for the motor you are using for the job. If you are unsure which bearing design is best for your work environment, contact an Aubearing expert to determine which bearing setup and motor is best for you. Please Whatapps +86 15006356216 or fill out our Quick Solution form to speak to an expert today.
