Bearing Manufacturer & Supplier
Specialize in ball bearings, roller bearings, thrust bearings, thin section bearings etc.
The Ultimate Guide to Bearing Torque
Bearings are precision parts that allow relative movement between mechanical parts. Ball bearings and roller bearings are the most common types of bearings, consisting of an inner ring, an outer ring, rolling elements and a retainer. They are key parts of rotating devices such as engines, gearboxes, car hubs, etc. They are designed to support rotating shafts and reduce friction between moving parts, thereby reducing energy loss and improving efficiency. Bearing torque is one of the key factors of bearing parameters. This blog aims to introduce bearing torque and provide constructive advice to help you choose the right bearing.
Table of Contents
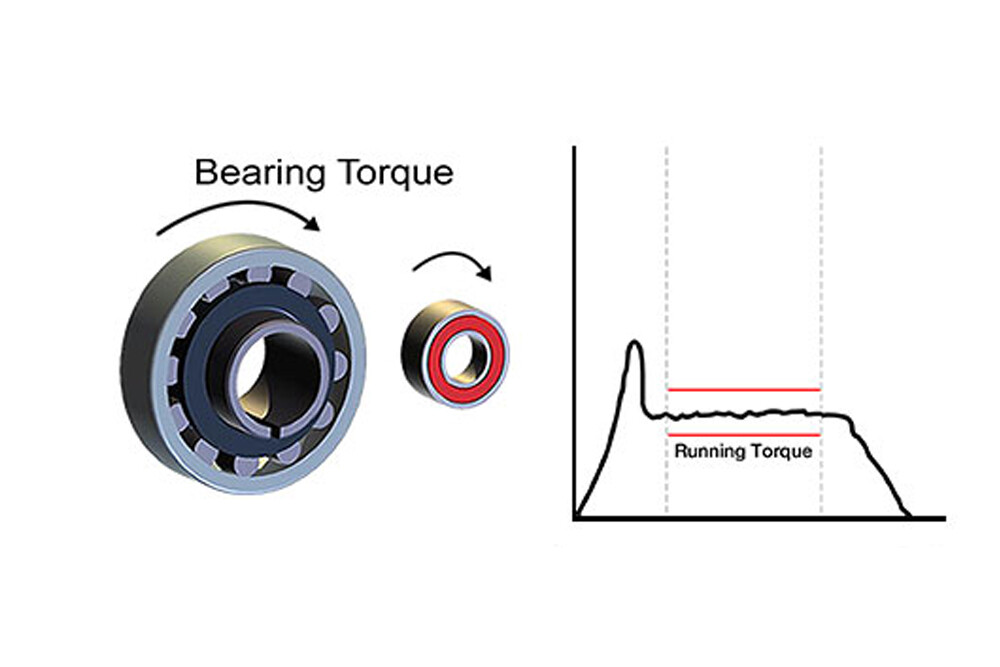
ToggleWhat is bearing torque?
Bearing torque is the force that overcomes internal friction in the bearing to initiate or maintain a rotational speed. Starting torque is the force that a bearing must overcome to start rotating. Running torque is the torque required for a bearing to start rotating and maintain rotation at a constant speed. It can be seen that the friction inside the bearing is the most important factor in the starting torque: the greater the friction inside the bearing, the greater the starting torque.

Factors affecting bearing torque
Bearing torque is based on tribological principles. Tribology is the study of friction, lubrication, and wear of interacting surfaces in relative motion. As a bearing rotates, it experiences different types of frictional resistance. To improve energy efficiency, we have been pursuing smaller bearing torques. Achieving optimal bearing torque is a complex task that requires careful consideration of bearing design factors and the characteristics of the bearing used. There are many factors that affect bearing torque, such as the type of bearing, the material the bearing is made of, bearing lubrication, preload, clearance, design parameters, and consideration of the environment in which the bearing operates. In order to effectively minimize bearing torque and improve the overall efficiency and life of the mechanical system to achieve smoother operation, reduce energy consumption and improve system performance, Aubearing determines the factors that affect bearing torque one by one.
Rolling Friction
Rolling bearings consist of an inner ring, an outer ring, rolling elements (such as balls or rollers) and a cage. When the bearing rotates, the rolling elements contact the raceways of the inner and outer rings of the bearing, causing rolling resistance or rolling friction. This resistance is caused by the deformation and sliding of the rolling elements and the presence of lubricant in the bearings.

Bearing type
The starting torque is different between different bearing types. The starting torque of ball bearings is generally lower than that of roller bearings. The internal rolling elements of a ball bearing are round and have “point contact” with the inner and outer rings. However, the rolling elements of roller bearings are cylindrical or elliptical rollers, and the contact with the inner and outer rings of the bearing is “line contact”. Compared with ball bearings, roller bearings have much greater torque.

Sealed or Shielded
Bearings often have seals or shields to prevent contaminants from entering and maintain lubrication. These seals create additional friction called seal friction. The amount of seal friction depends on the design, material and condition of the seal. Generally speaking, the friction resistance of the rubber seal will be greater than the friction resistance of the metal shield.

Lubricant viscosity
Typically, bearings require lubrication to reduce friction and wear. The lubricant used can be oil or grease, but they have a specific viscosity. The viscosity of a lubricant creates a certain amount of resistance. Obviously, the viscous the lubricant, the greater the rotational resistance and the greater the starting torque required. In addition, if the equipment has not been used for a long time, the lubricant may be squeezed out from between the seal and the shaft, and the starting torque may be much greater. Generally speaking, the resistance of grease will be greater than the resistance of lubricating oil.

Shaft surface finish
Shaft surface finish is also one of the factors affecting bearing torque. It is known that the rougher the shaft surface, the higher the torque. One phenomenon that increases starting torque is adhesion between contact surfaces if the shaft is at rest for a long period of time. Additionally, corrosion of the shaft sometimes causes a bond between the bearing contact surfaces, which of course must be broken before rotation can begin.

Bearing material
Bearing material also affects torque. Lightweight metal and plastic retainer provides minimal torque at low and medium speeds. Generally speaking, phenolic and sintered nylon cages have lower torque at high speeds. Very low contact angle or radial clearance values indicate high torque because the geometric errors inherent in the bearing raceways and balls can cause unstable changes in stress and thus in the friction level. It can be seen that angular contact bearings have very high contact angles and correspondingly higher torque levels.

Calculate bearing torque
Calculating the value of bearing torque is important to optimize your system and will help select the best bearings and configuration. You can calculate an approximation of friction torque using this simple formula.
Ball bearing torque calculation
Radial ball bearings: 0.5 x 0.0013 x radial load (Newtons) * x bearing bore diameter (mm)
Thrust ball bearing: 0.5 x 0.0011 x axial load (Newtons) * x bearing bore diameter (mm) )
This formula for calculating bearing torque is only valid if the ball bearing is fully lubricated, has no contact seals, and is subject to low speeds and low loads. For radial ball bearings, the axial load should be less than 20% of the radial load, while for thrust bearings, the load should be purely axial. The unit of measurement is Newton millimeters (Nmm). This is a composite unit of torque that corresponds to the torque produced by exerting a force of 1 Newton (approximately 0.1 Kgf) on an arm at a distance of 1 mm. If you require accurate ball bearing torque data taking into account speed and lubricant viscosity, please contact Aubearing.
Calculation of roller bearing torque
To calculate the torque of a roller bearing, we need to know several terminology concepts.
Radial load is the load perpendicular to the axis of the bearing.
Axial load is a force acting parallel to the axis of the shaft.
Calculating the torque of a roller bearing also requires factors such as the number and size of rolling elements, contact angle and raceway size. Additionally, bearing geometry is a key factor affecting torque calculations. Of course, the roller bearing friction coefficient is essential for calculating the torque of a roller bearing. They represent the resistance to movement caused by friction between rolling elements and raceways. Friction coefficients for specific bearing types and lubrication conditions can be found on the bearing manufacturer’s website or catalog.
Torque (M)=Fr*d*μ+Fa*Dm*μa
M stands for torque
Fr represents radial load
d represents the rolling element diameter
μ represents the rolling element friction coefficient
Fa represents axial load
Dm represents the average diameter of the bearing
μa represents the axial friction coefficient
By knowing the calculated torque of a roller bearing, engineers can roughly assess whether the bearing can handle expected loads, operate within acceptable torque limits, and maintain efficient motion. Proper bearing sizing can prevent premature wear, excessive heating and potential system failure.
Conclusion
Understanding the factors that affect bearing torque and accurately calculating bearing torque will help select the correct bearing. Manufacturer’s guidelines must be consulted and followed to obtain accurate torque specifications for a specific application to ensure optimal performance and system reliability. As we all know, Aubearing is a trustworthy bearing manufacturer in China and a world-renowned online bearing store, providing comprehensive solutions for the bearings you need.
