Bearing Manufacturer & Supplier
Specialize in ball bearings, roller bearings, thrust bearings, thin section bearings etc.
Guide to Bearings in Seawater
With the continuous development and utilization of marine resources, the demand for marine engineering equipment is growing. As the core component of mechanical equipment, the performance and quality of bearings are crucial to the operation of the entire equipment. In the marine environment, corrosion is a common problem, so bearings used in marine engineering must cope with the ever-present risk of corrosion. Due to the corrosive power of seawater, the selection of bearings must balance load capacity and corrosion resistance to extend the service life of the bearings.
Table of Contents
ToggleHazards of Seawater Corrosion
Subsea applications are characterized by continuous harsh conditions and extreme environments. In the marine environment, various applications involve propeller shafts and components for underwater robots and telecommunications systems. However, in water, salt and harsh conditions, it is not enough to just choose any bearing – it is essential to choose the right bearing for optimal performance and durability. The World Corrosion Organization reports that the global cost of corrosion is a staggering $2.2 trillion per year, equivalent to than 3% of the world’s GDP. When bearings in underwater industrial applications begin to corrode, a series of harmful effects will be triggered.

Corrosion accelerates the wear of bearing raceways, rolling elements and cages. This increased wear, combined with compromised surface integrity, increases the bearing’s susceptibility to the intrusion of abrasive particles and contaminants. These contaminants can further increase wear and damage to critical components such as seals, gears and other bearings, ultimately leading to further failures and increased maintenance and replacement costs. Rapid intervention and the use of corrosion-resistant bearings are critical to mitigating these risks and ensuring the integrity and longevity of subsea equipment.
Bearing materials suitable for marine environment
Corrosion-resistant bearing materials must have high corrosion resistance and wear resistance so that they can be used for a long time in salt spray, seawater and other corrosive media. Commonly used corrosion-resistant bearing materials include stainless steel, ceramics and plastics.
Stainless steel materials have good corrosion resistance and wear resistance and are commonly used bearing materials in marine engineering equipment. Stainless steel bearings are a type of bearing widely used in water. Its material has the characteristics of corrosion resistance, acid and alkali resistance, oxidation resistance and high temperature resistance, which are very suitable for water environments such as oceans, rivers and lakes. And stainless steel bearings can adapt to larger loads and speeds. In practical applications, they can not only reduce the number of maintenance times, but also increase the service life of equipment.
440 stainless steel is a high-carbon, high-chromium martensitic stainless steel that has a certain resistance to seawater or salt spray, has good corrosion resistance and wear resistance, and is suitable for corrosion and wear in marine environments. However, their resistance to seawater or salt spray is limited. By passivating them, their corrosion resistance can also be improved. Passivation is a metal finishing process that uses nitric acid or citric acid to remove free iron on the surface. Chemical treatment results in a protective oxide layer that is less likely to react chemically with air and cause corrosion. However, unless protected, this will eventually corrode in a marine environment.

316 stainless steel is a low-carbon, high-chromium, nickel stainless steel material with good corrosion resistance and wear resistance, suitable for corrosion and wear in a marine environment. Compared with 440 stainless steel, 316 stainless steel is cheaper, so it is widely used in marine engineering equipment.

Application cases of stainless steel bearings
Stainless steel bearings are widely used in marine engineering, including ship propellers, offshore platforms, seawater pumps, valves and pipelines. Its excellent corrosion resistance and wear resistance can ensure the stability and reliability of equipment in harsh marine environments. When selecting stainless steel bearings, it is necessary to comprehensively consider the specific use environment and working conditions to select the most suitable bearing material and type.

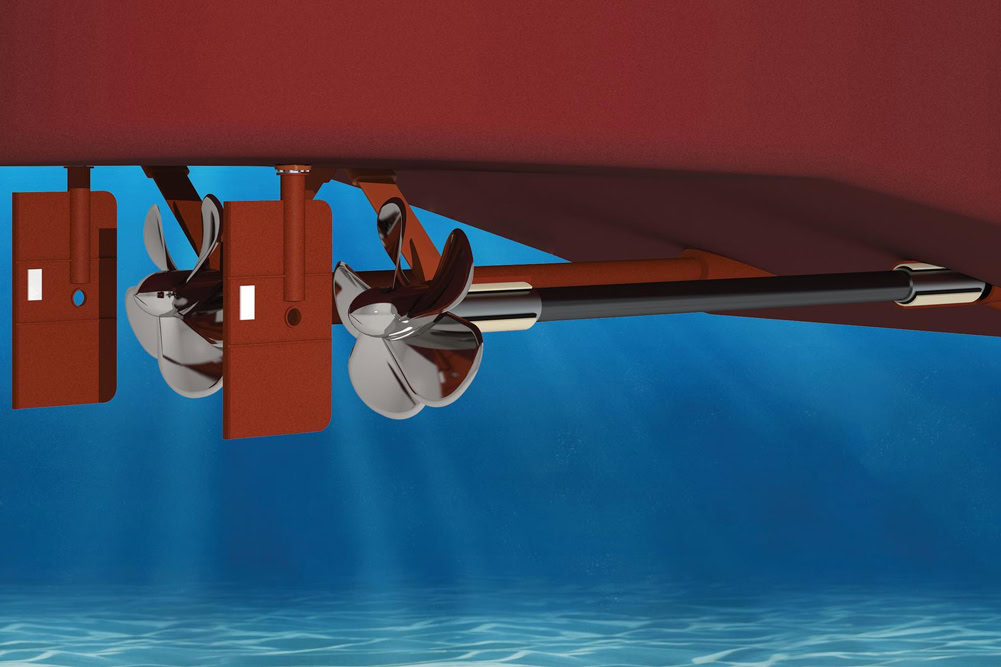
Ship Propeller
Ship propellers are key components of ship power systems and need to withstand seawater corrosion and long-term operation wear. Stainless steel bearings are ideal for ship propellers due to their excellent corrosion resistance and wear resistance. Commonly used stainless steel bearing materials include 440 stainless steel and 316 stainless steel. These materials have good corrosion resistance in seawater and can ensure the long-term stable operation of the propeller.

Offshore platform
Offshore platforms are important facilities for offshore operations and need to withstand a variety of harsh environments such as seawater corrosion and wind and wave impact. The application of stainless steel bearings on offshore platforms is mainly concentrated in key transmission components, such as bogies, elevators, etc. The corrosion resistance and wear resistance of stainless steel bearings can ensure the stability and reliability of offshore platforms in harsh environments.

Seawater pump
Seawater pumps are commonly used equipment in marine engineering, used to extract seawater for desalination, cooling and other treatments. The application of stainless steel bearings in seawater pumps is mainly concentrated in key parts such as impellers and main shafts. The combination of CF-8M cast stainless steel impellers (equivalent to 316 stainless steel) and 316 stainless steel main shafts can operate stably for a long time in seawater environments, reducing corrosion and wear.

Valves and pipelines
Valves and pipelines are important components for conveying fluids in marine engineering and need to withstand conditions such as seawater corrosion and high pressure. The application of stainless steel bearings in valves and pipelines is mainly concentrated in control mechanisms and sealing components. The corrosion resistance and sealing performance of stainless steel bearings can ensure the stable operation of valves and pipelines in marine environments, preventing leakage and corrosion.
Full ceramic bearings are made of zirconia or silicon nitride materials, which have the characteristics of high corrosion resistance, high hardness and high wear resistance, and are suitable for corrosion and wear in marine environments. However, Full ceramic bearings are expensive and relatively brittle, so care must be taken to avoid impact during use. Full ceramic bearings are not recommended in environments that must withstand heavy impact loads.

Nonmagnetic
One of the main advantages of ceramic bearings is their non-magnetic nature, which plays a vital role in preventing the transmission of electromagnetic interference signals. Because undersea telecommunications systems rely on accurate data transmission over long distances, any magnetic interference can cause signal interruptions and data loss. By using non-magnetic ceramic bearings, these systems maintain the integrity of signal transmission, ensuring uninterrupted communications between continents and improving the overall reliability and performance of undersea telecommunications networks.

Reduce friction and wear
Compared with steel bearings, ceramic bearings have a significantly lower friction coefficient, which reduces energy consumption, increases the efficiency of the entire system, and extends the service life. Both zirconium oxide (ZrO2) and silicon nitride (Si3N4) have low friction coefficients, and they can even be used without lubrication in low-speed applications. The special hardness of ceramic materials also helps reduce wear rates, extending bearing life and reducing downtime for maintenance and replacement.
Resistant to debris and contamination
The subsea environment often puts bearings at risk from debris, sand and other contaminants. In this case, conventional steel bearings will suffer accelerated wear and failure. Because ceramic bearings are much harder, their resistance to particle intrusion is increased, although care should be taken to prevent contaminants from entering any bearing to ensure reliable operation. This feature reduces the risk of failure and increases the durability of subsea equipment.
Ceramic bearings provide excellent corrosion resistance in marine applications. Because ceramic bearings are not affected by seawater, they can be used in permanently submerged marine environments and can handle higher loads. Ceramic bearings are mainly used in environments that are too unfavorable for steel bearings. Due to the brittleness of ceramics, they are unlikely to withstand large impact loads.

Plastic bearings
Plastic bearings are a type of bearing that is lightweight, low-noise, easy to install and maintenance-free, and are often used in equipment such as small water pumps. However, plastic materials have low strength and low load capacity, and are not suitable for high-load and high-speed rotation. The capacity of plastic bearings can be increased by using alternative materials such as PEEK, but these materials are still classified as semi-precision, low-load bearings.

Rubber bearings
Rubber bearings are also a type of bearing that is widely used in water. Rubber has excellent elasticity, tensile strength, and self-lubricating properties. Rubber bearings have a low friction coefficient under water lubrication, and can effectively prevent or slow down impact and reduce noise. Rubber bearings have good seismic resistance and can adapt to large displacements and deformations. They are widely used in environments such as submarine pipelines that need to absorb shock and vibration.
Conclusion
Bearings are very important components in marine engineering. The marine environment places extremely high demands on the quality and reliability of bearings, so special bearings suitable for marine environments need to be selected. These bearings have friendly characteristics such as corrosion resistance and impact resistance, which can ensure the stability and reliability of bearings. Selecting the right bearing type and specification in marine engineering can ensure the safe and stable operation of marine engineering. 440 grade stainless steel bearings are suitable for marine environments, but they need passivation treatment; 316 grade stainless steel bearings have lower load and speed ratings; ceramic bearings are corrosion-resistant but expensive and fragile; acetal resin bearings and plastic bearings are suitable for low-precision, low-load and low-speed applications.
