Bearing Manufacturer & Supplier
Specialize in ball bearings, roller bearings, thrust bearings, thin section bearings etc.
Guide to Ball Bearing Size Charts
Bearings are one of the most indispensable components in any industrial machinery. There is a legend that “bearings are the food of industry”. These high-precision ball bearings are essential for reducing friction and carrying loads during rotational motion. You should have at least one bearing in many industrial applications. There are many bearing manufacturers in the world, such as SKF, FAG, NST, NTN, etc., who produce thousands of types of bearings, including ball bearings, cylindrical roller bearings, tapered roller bearings, needle roller bearings, thrust ball bearings, and self-aligning bearings. Roller bearings, thin section bearings and automotive bearings, etc. Among them, ball bearings are the most common bearings, but each model has its own characteristics and advantages, making it only suitable for certain specific uses and applications and not suitable for other operating environments.
Proper selection and installation of bearings is very important to ensure optimal machine performance. The right bearings not only improve the performance of your machine, but also extend its service life while reducing downtime and maintenance costs. On the contrary, choosing the wrong bearing may increase power consumption, increase maintenance, greatly reduce the efficiency of the machine, and may even lead to expensive downtime. If you don’t consult a bearing expert when it comes to bearing selection, you may be paying the price. However, choosing the right bearing for the application is not always easy. There are many different factors to consider when selecting a bearing, such as speed, load and operating conditions.
The first thing to consider when selecting a bearing is the available mounting space. No matter how well a bearing fits your application requirements, if there is no available space, it cannot be installed. The available space will determine the bore and outer diameter of the bearing you choose, so it is important to know this information before selecting a bearing. It plays a key role in selecting the right bearing for a specific application, ensuring optimal performance and service life of your equipment. To this end, AUB has summarized the size table of the most widely used ball bearings based on many years of bearing manufacturing experience, allowing you to understand the dimensions of manufacturing ball bearings at a glance.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat are the dimensions of a standard ball bearing?
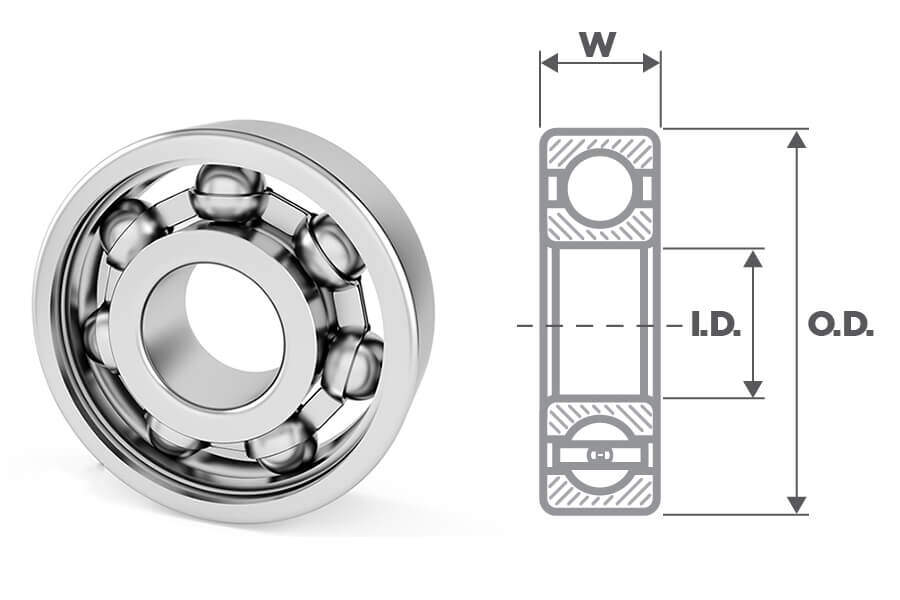
Standard ball bearing dimensions vary widely depending on the type of bearing and application. Ball bearings are used in all industries and therefore need to be sized for applications ranging from skateboard wheels to offshore drilling rigs. So, how are standard bearing sizes determined? Generally speaking, ball bearing dimensions are measured by inner diameter, outer diameter, and width; bearing measurements are completed in the following order: ID x OD x W. These measurements are usually in millimeters and inches. In fact, most manufacturers and suppliers offer bearing measurements in both imperial and metric systems. Each combination of measurements corresponds to a bearing serial number. Ball bearing size charts can be used to find measurements for a specific bearing. Of these, the 6200 and 6300 series are the most commonly used ball bearings, typically ranging in size from 10 x 30 x 9 mm (0.394 x 1.181 x 0.354 in) to 150 x 320 x 65 mm (5.906 x 12.598 x 2.559 in).

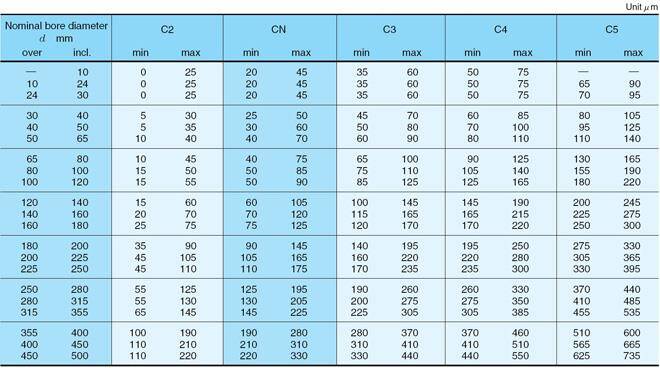
Bearing clearance
It is worth noting that you also need to know the clearance of the bearing: normal clearance, no suffix; C3 is greater than the normal clearance. C3 clearance allows bearings to run faster and at higher temperatures without failure. Of course, you can also customize clearances, so if you have a special type of bearing, please contact us.
C2: Below standard;
C3: Larger gap;
C4: larger than C3.
Chance often hears about bearing guards and seals, which protect the inside of the bearing from debris or contaminants; these include open, sealed on both sides (-2RS), sealed on one side (-RS), shielded on both sides ( -ZZ), one side shield (-Z) and retaining ring (NR). Both metal guards and rubber seals can be used individually to protect only one side of the bearing or both sides, depending on your application requirements.

Common metric size ball bearings include:
6000 series: aperture range 10 mm
6200 series: hole diameter range 10 to 30 mm
6300 Series: Bore diameter range 10 to 35 mm
6800 series: bore diameter range 10 to 80 mm
6900 Series: Bore diameter range 10 to 100 mm
For imperial sizes, common series include:
R Series: Bore diameter 0.1875 to 0.5 inches
1600 Series: Bore size range 0.1875 to 0.5 in.
16000 Series: Bore diameter range 10.319 to 12.7 mm
63000 Series: Bore diameter range 10.319 to 12.7 mm
Main parameters included in the bearing size charts
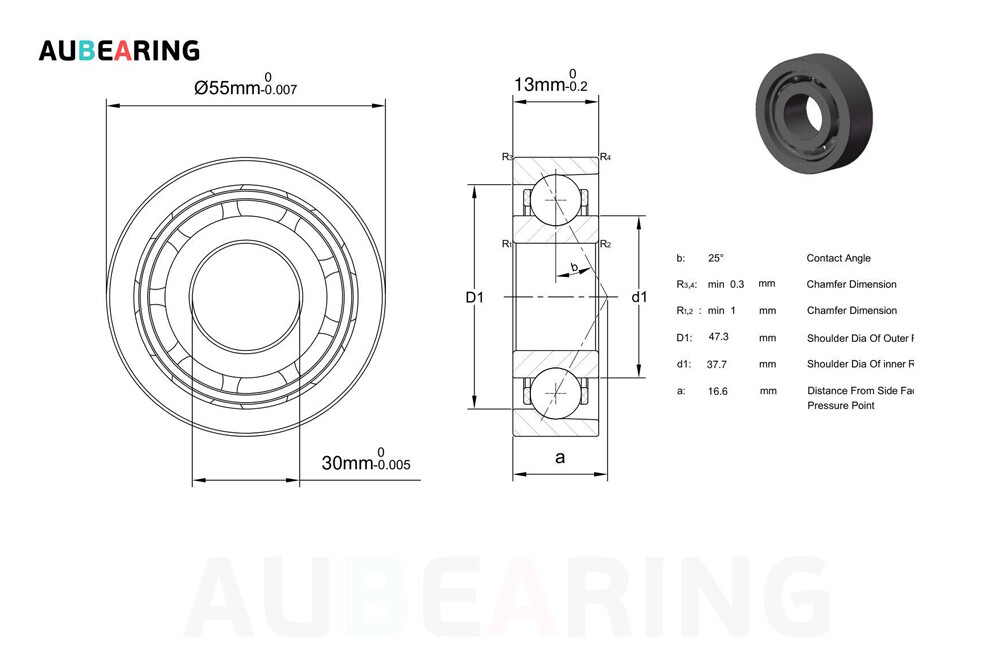
Bearing dimensions. Dimensional charts provide basic measurements for ball bearings such as bore diameter (inner diameter), outer diameter, and width. These dimensions determine the bearing’s compatibility with its intended shaft and housing.
specified load. Ball bearings bear radial and axial loads during operation. The load rating in the dimension table indicates the maximum load capacity the bearing can withstand before premature failure.
Speed rating. The speed class defines the maximum speed at which a bearing can operate without causing excessive heating or premature wear.
clearance. Bearing clearance is the internal clearance between the balls and raceways. It affects the axial and radial clearance as well as the thermal expansion characteristics of the bearing.

6000 series bearings size charts
The main dimensions of the ball bearings of the 6000 series comply with DIN 625-1. The small ball bearings of the 6000 series can support radial loads despite their low weight. Compared with the deep groove ball bearings of the 6300 medium series, with the same inner diameter, the 6000 series bearings require smaller installation space, weigh only half of the deep groove ball bearings of the 63 medium series, and allow higher rotational speeds. Often used in electric motors.
Size | Inner Dimension (mm) | Outer Dimension (mm) | Width (mm) | Dynamic (Cr) | Static (Cor) | Weight (lb) |
10 | 26 | 8 | 1030 | 445 | 0.042 | |
12 | 28 | 8 | 1147 | 535 | 0.048 | |
15 | 32 | 9 | 1254 | 641 | 0.068 | |
17 | 35 | 10 | 1349 | 731 | 0.088 | |
20 | 42 | 12 | 2109 | 1129 | 0.150 | |
25 | 47 | 12 | 2248 | 1315 | 0.172 | |
30 | 55 | 13 | 2967 | 1866 | 0.242 | |
35 | 62 | 14 | 3642 | 2360 | 0.0326 | |
40 | 68 | 15 | 3867 | 2653 | 0.407 | |
45 | 75 | 16 | 4721 | 3327 | 0.506 | |
50 | 80 | 16 | 4946 | 3642 | .0568 | |
55 | 90 | 18 | 6789 | 4901 | .0796 | |
60 | 95 | 18 | 7081 | 5440 | .0847 | |
65 | 100 | 18 | 6857 | 5665 | 0.957 | |
70 | 110 | 20 | 8565 | 6947 | 1.324 | |
75 | 115 | 20 | 8902 | 7531 | 1.404 | |
80 | 125 | 22 | 10701 | 8947 | 1.870 | |
85 | 130 | 22 | 11128 | 9689 | 1.958 | |
90 | 140 | 24 | 13084 | 11173 | 2.552 | |
95 | 145 | 24 | 13578 | 12117 | 2.662 | |
100 | 150 | 24 | 13533 | 12185 | 2.750 | |
105 | 160 | 26 | 16254 | 14792 | 3.498 | |
110 | 170 | 28 | 18434 | 16411 | 4.312 | |
120 | 180 | 28 | 18659 | 17535 | 4.796 | |
130 | 200 | 33 | 23380 | 22481 | 7.326 | |
140 | 210 | 33 | 24279 | 24279 | 7.832 | |
150 | 225 | 35 | 27427 | 28101 | 9.636 |
6200 series bearings size charts
The main dimensions of 6200 series ball bearings comply with DIN 625-1 standards. The 6200 lightweight series ball bearings are also lighter in weight but can still support relatively higher radial loads than the 6000 series. Compared with the 63 and 64 series deep groove ball bearings, the outer diameter of the 6200 series ball bearings is relatively smaller, so it requires less installation space under the same inner diameter and allows slightly higher rotational speeds. 6200 series ball bearings are commonly used in food processing, household appliances, chemical and pharmaceutical industries, motorcycles, pumps, fans, water treatment and many other industrial applications
Size | Inner Dimension (mm) | Outer Dimension (mm) | Width (mm) | Dynamic (Cr) | Static (Cor) | Weight (lb) |
10 | 30 | 9 | 1147 | 535 | 0.070 | |
12 | 32 | 10 | 1533 | 686 | 0.077 | |
15 | 35 | 11 | 1720 | 836 | 0.099 | |
17 | 40 | 12 | 2154 | 1075 | 0.141 | |
20 | 47 | 14 | 2878 | 1495 | 0.227 | |
25 | 52 | 15 | 3147 | 1771 | 0.279 | |
30 | 62 | 16 | 4384 | 2585 | 0.440 | |
35 | 72 | 17 | 5733 | 3417 | 0.634 | |
40 | 80 | 15 | 6632 | 4047 | 0.810 | |
45 | 85 | 19 | 7081 | 4609 | 0.915 | |
50 | 90 | 20 | 7868 | 5216 | 1.019 | |
55 | 100 | 21 | 9757 | 6609 | 1.335 | |
60 | 110 | 22 | 11780 | 8138 | 1.723 | |
65 | 120 | 23 | 12859 | 9015 | 2.178 | |
70 | 125 | 24 | 13983 | 9914 | 2.354 | |
75 | 130 | 25 | 15152 | 10858 | 2.596 | |
80 | 140 | 26 | 16344 | 11915 | 3.080 | |
85 | 150 | 28 | 18884 | 13916 | 3.938 | |
90 | 160 | 30 | 21604 | 16074 | 4.730 | |
95 | 170 | 32 | 24504 | 18412 | 5.764 | |
100 | 180 | 34 | 27427 | 20930 | 6.908 | |
105 | 190 | 36 | 29899 | 23605 | 8.140 | |
110 | 200 | 38 | 32372 | 26303 | 9.592 | |
120 | 215 | 40 | 32822 | 27427 | 12.386 | |
130 | 230 | 40 | 37318 | 32822 | 13.728 | |
140 | 250 | 42 | 39566 | 37318 | 17.754 | |
150 | 270 | 45 | 39566 | 38217 | 22.660 |
6300 series bearings size charts
The main dimensions of 6300 series ball bearings comply with DIN 625-1 standards. Ball bearings in the 63 medium series provide a balanced ratio between radial load carrying capacity, required installation space, weight and permitted rotational speed. Therefore, 6300 ball bearings are one of the most versatile bearings. The functionality of the 6300 series is similar to that of the 6200 series. The use of larger balls combined with larger raceway sizes allows the bearings to withstand greater radial and thrust loads for a given bore size. The 6300 Series is available in open, shielded, sealed or snap-ring versions upon request. The 6300 Series features larger balls and heavier races to provide greater radial, thrust and combined load capabilities. 6300 Series Commonly used in food processing, household appliances, chemical and pharmaceutical industries, motorcycles, pumps, fans, water treatment and many other industrial applications
Size | Inner Dimension (mm) | Outer Dimension (mm) | Width (mm) | Dynamic (Cr) | Static (Cor) | Weight (lb) |
6300 | 10 | 35 | 11 | 1720 | 782 | 0.12 |
6301 | 12 | 37 | 12 | 2185 | 1142 | 0.13 |
6302 | 15 | 42 | 13 | 2585 | 1218 | 0.18 |
6303 | 17 | 47 | 14 | 3035 | 1479 | 0.24 |
6304 | 20 | 52 | 15 | 3552 | 1771 | 0.31 |
6305 | 25 | 62 | 17 | 4991 | 2585 | 0.48 |
6306 | 30 | 72 | 19 | 6070 | 3417 | 0.77 |
6307 | 35 | 80 | 21 | 7464 | 4316 | 1.00 |
6308 | 40 | 90 | 23 | 9172 | 5395 | 1.41 |
6309 | 45 | 100 | 25 | 11870 | 7149 | 1.92 |
6310 | 50 | 110 | 27 | 13938 | 8610 | 2.35 |
6311 | 55 | 120 | 29 | 16096 | 10116 | 3.01 |
6312 | 60 | 130 | 31 | 18412 | 11735 | 3.74 |
6313 | 65 | 140 | 33 | 20840 | 13466 | 4.58 |
6314 | 70 | 150 | 35 | 23380 | 15322 | 5.54 |
6315 | 75 | 160 | 37 | 25403 | 17355 | 6.64 |
6316 | 80 | 170 | 39 | 27651 | 19491 | 7.90 |
6317 | 85 | 180 | 41 | 29899 | 21761 | 9.31 |
6318 | 90 | 190 | 43 | 32148 | 24054 | 10.80 |
6319 | 95 | 200 | 45 | 34396 | 26752 | 12.47 |
6320 | 100 | 215 | 47 | 38892 | 31698 | 15.40 |
6321 | 105 | 225 | 49 | 41365 | 34396 | 17.71 |
6322 | 110 | 240 | 50 | 46086 | 40465 | 20.99 |
6324 | 120 | 260 | 55 | 47659 | 42714 | 28.16 |
6326 | 130 | 280 | 58 | 51256 | 48559 | 40.26 |
6328 | 140 | 300 | 62 | 57326 | 55078 | 49.06 |
6330 | 150 | 320 | 65 | 64070 | 67442 | 58.74 |
6400 series bearings size charts
The main dimensions of 6400 series ball bearings comply with DIN 625-1 standards. Compared to 60, 62 and 63 series deep groove ball bearings, 64 series ball bearings can handle higher load ratings for the same bore diameter. For example, they have twice the load-carrying capacity compared to 62 lightweight series deep groove ball bearings. AUB manufactures bearings to meet virtually any operating accuracy requirement and application speed: AUB manufactures deep groove ball bearings with Abec tolerances of 1-9, internal clearances from C2 to C4, and a variety of different cage designs, including J-type , W type, RJ type, TW type, etc.
Item # | (d) Bore Diameter | (D) Outer Diameter | (B) Width | Seal | Internal Clear ance |
6403-2RS | 17mm | 62mm | 17mm | 2RS | CN |
6403-OIL | 17mm | 62mm | 17mm | open | CN |
6403-ZZ | 17mm | 62mm | 17mm | ZZ | CN |
6404-2RS | 20mm | 72mm | 19mm | 2RS | CN |
6404-OIL | 20mm | 72mm | 19mm | open | CN |
6404-ZZ | 20mm | 72mm | 19mm | ZZ | CN |
6405-2RS | 25mm | 80mm | 21mm | 2RS | CN |
6405-OIL | 25mm | 80mm | 21mm | open | CN |
6405-Z | 25mm | 80mm | 21mm | Z | CN |
6405-ZZ | 25mm | 80mm | 21mm | ZZ | CN |
The main dimensions of the 6700 series thin section ball bearings comply with DIN 625-1 standards. Series 67 bearings are still smaller than Series 68 thin-section bearings, which have an ultra-thin square cross-section for the same bore diameter. Their outer diameter is very small compared to their inner diameter, and they are very narrow. Therefore, relatively large shafts and shaft diameters can be installed in extremely limited installation spaces, suitable for relatively high speeds.
Size | Inner Dimension (mm) | Outer Dimension (mm) | Width (mm) | Dynamic (Cr) | Static (Cor) | Weight (lb) |
6701 | 12 | 18 | 4 | 205 | 119 | 0.004 |
6702 | 15 | 21 | 4 | 191 | 110 | 0.005 |
6703 | 17 | 23 | 4 | 216 | 137 | 0.006 |
6704 | 20 | 27 | 4 | 232 | 162 | 0.010 |
6705 | 25 | 32 | 4 | 246 | 187 | 0.015 |
6706 | 30 | 37 | 4 | 263 | 220 | 0.018 |
6707 | 35 | 44 | 5 | 416 | 366 | 0.021 |
The main dimensions of 6800 thin section ball bearings comply with DIN 625-1 standards. The 68 series thin-section bearings are still smaller in size than the 69 series thin-section bearings, with an ultra-thin square cross-section at the same inner diameter. Their outer diameter is very small compared to their inner diameter, and they are very narrow. Therefore, the relatively large shaft and shaft diameter of the 6800 thin-section ball bearing can be installed in an extremely limited installation space, is very light, and is suitable for relatively high speeds.
Size | Inner Dimension (mm) | Outer Dimension (mm) | Width (mm) | Dynamic (Cr) | Static (Cor) | Weight (lb) |
6800 | 10 | 19 | 5 | 411 | 208 | 0.011 |
6801 | 12 | 21 | 5 | 432 | 234 | 0.0132 |
6802 | 15 | 24 | 5 | 468 | 286 | 0.0154 |
6803 | 17 | 26 | 5 | 632 | 387 | 0.0176 |
6804 | 20 | 32 | 7 | 899 | 555 | 0.0418 |
6805 | 47 | 37 | 7 | 967 | 663 | 0.0484 |
6806 | 30 | 42 | 7 | 1057 | 821 | 0.0572 |
6807 | 35 | 47 | 7 | 1102 | 910 | 0.0638 |
6808 | 40 | 52 | 7 | 1113 | 944 | 0.0726 |
6809 | 45 | 58 | 7 | 1394 | 1214 | 0.088 |
6810 | 50 | 65 | 7 | 1484 | 1371 | 0.1144 |
6811 | 55 | 72 | 9 | 1978 | 1821 | 0.1826 |
6812 | 60 | 78 | 10 | 2585 | 2383 | 0.2288 |
6813 | 65 | 85 | 10 | 2675 | 2585 | 0.2772 |
6814 | 70 | 90 | 10 | 2720 | 2675 | 0.2948 |
6815 | 75 | 95 | 10 | 2810 | 2900 | 0.3124 |
6816 | 80 | 100 | 10 | 2855 | 2990 | 0.33 |
6817 | 85 | 110 | 13 | 4204 | 4271 | 0.5852 |
6818 | 90 | 115 | 13 | 4271 | 4429 | 0.6138 |
6819 | 95 | 120 | 13 | 4339 | 4429 | 1.551 |
6820 | 100 | 125 | 13 | 4406 | 4766 | 0.6798 |
6821 | 105 | 130 | 13 | 4451 | 5373 | 0.7128 |
6822 | 110 | 140 | 16 | 6317 | 6902 | 1.3332 |
6824 | 120 | 150 | 16 | 6519 | 7419 | 1.441 |
6826 | 130 | 165 | 18 | 8295 | 9262 | 2.0658 |
6828 | 140 | 175 | 18 | 8588 | 9981 | 2.2 |
6830 | 150 | 190 | 20 | 10746 | 12342 | 3.08 |
The main dimensions of the 6900 series thin section ball bearings comply with DIN 625-1 standards. Series 69 thin section bearings are significantly smaller than Series 60, 62, 63 and 64 deep groove ball bearings with a thin square cross-section of the same bore diameter. As a result, relatively large shafts and shaft diameters can be installed in extremely limited installation spaces. They are very light and suitable for relatively high speeds.
Rubber seals (RS/2RS) provide optimal sealing action and increased friction. Metal seals (Z/ZZ) are suitable for higher speeds, but since they are non-contact seals their sealing effect is limited. Open sealless bearings are suitable for very high speeds and are easier to re-lubricate. However, they are susceptible to staining.
Size | Inner Dimension (mm) | Outer Dimension (mm) | Width (mm) | Dynamic (Cr) | Static (Cor) | Weight (lb) |
6900 | 10 | 22 | 6 | 652 | 326 | 0.010 |
6901 | 12 | 24 | 6 | 967 | 506 | 0.011 |
6902 | 15 | 28 | 7 | 1034 | 573 | 0.017 |
6903 | 17 | 30 | 7 | 1428 | 832 | 0.018 |
6904 | 20 | 37 | 9 | 1574 | 1023 | 0.036 |
6905 | 47 | 42 | 9 | 1630 | 1124 | 0.041 |
6906 | 30 | 47 | 9 | 2450 | 1742 | 0.045 |
6907 | 35 | 55 | 10 | 3080 | 2237 | 0.073 |
6908 | 40 | 62 | 12 | 3170 | 2450 | 0.112 |
6909 | 45 | 68 | 12 | 3260 | 2630 | 0.132 |
6910 | 50 | 72 | 12 | 3732 | 3170 | 0.133 |
6911 | 55 | 80 | 13 | 4541 | 3889 | 0.185 |
6912 | 60 | 85 | 13 | 3912 | 3619 | 0.104 |
6913 | 65 | 90 | 13 | 5328 | 4766 | 0.211 |
6914 | 70 | 100 | 16 | 5485 | 5081 | 0.342 |
6915 | 75 | 105 | 16 | 5620 | 5395 | 0.363 |
6916 | 80 | 110 | 16 | 7171 | 6654 | 0.382 |
6917 | 85 | 120 | 18 | 7374 | 7104 | 0.535 |
6918 | 90 | 125 | 18 | 7576 | 7531 | 0.565 |
6919 | 95 | 130 | 18 | 10116 | 9419 | 0.705 |
6920 | 100 | 140 | 20 | 10454 | 10071 | 0.960 |
6921 | 105 | 145 | 20 | 10768 | 10746 | 1.000 |
6922 | 110 | 150 | 20 | 12859 | 12792 | 1.040 |
6924 | 120 | 165 | 22 | 15647 | 15737 | 1.410 |
6926 | 130 | 180 | 24 | 16029 | 16816 | 1.860 |
6928 | 140 | 190 | 24 | 20997 | 21199 | 1.980 |
6930 | 150 | 210 | 28 | 21000 | 326 | 3.050 |
Why do bearings come in so many sizes?
As mentioned previously, bearing size depends on the size of the shaft and the application requirements. Bearing size can greatly affect the performance and capabilities of a ball bearing; therefore, different industries use different sizes. Generally speaking, smaller ball bearings have limited load capabilities. They are used in applications where space efficiency is important than load capacity. Miniature bearings are typically constructed as precision ball bearings and are used in extremely small applications such as medical instruments, robotics, or semiconductor equipment. On the other hand, larger bearings have greater load capacity. They are used in heavy industry such as agricultural machinery, mining and drilling equipment or heavy power tools. Many manufacturers also offer custom bearing size options for very specific applications with unique requirements.

What are the consequences of mismatched bearing sizes?
When selecting the appropriate ball bearing, be sure to use the bearing size chart to find the appropriate size for your application. If the bearing size does not match the application, serious problems will occur:
Fast wear due to friction
Reduced efficiency
Overheating
Vibration and noise
Frequent breakdowns and downtime
Security risks
Increased friction and wear
Choosing an inappropriate bearing size can cause misalignment between the bearing and the shaft and increase friction, which can cause rapid wear and deterioration of bearing components, significantly shortening their service life.
Reduced efficiency
If the bearing size is too small or too large, the bearing may not distribute the load evenly. Uneven load distribution can cause the bearing to operate inefficiently because the bearing may not be able to handle the applied forces and rotations as expected. As a result, mechanical efficiency may be affected, resulting in reduced overall performance.
Overheat
Improperly sized bearings may not dissipate heat effectively. Excessive heat can be generated due to friction, causing the bearings and surrounding components to overheat. Increased temperatures can reduce lubricant performance, weaken materials, and ultimately lead to bearing failure.
Vibration and noise
Bearings with mismatched dimensions can cause vibration and noise during operation. These vibrations not only affect the smoothness of the machinery but can also cause structural damage over time. Additionally, the resulting noise may be a sign of misalignment or uneven load distribution, indicating potential problems with bearing performance.
Frequent breakdowns and downtime
Bearings that do not meet dimensional requirements are likely to fail prematurely. Replacing failed bearings and resolving the resulting problems can cause costly downtime in industrial processes, impacting productivity and profitability.
Security Risk
In critical applications such as automotive or aerospace systems, the use of improperly sized bearings can pose serious safety risks. Sudden failure caused by bearing mismatch can lead to accidents, especially at high speeds or high loads, endangering the safety of equipment and personnel.
To avoid these problems, it is critical to consult the bearing manufacturer’s specifications and appropriate dimensional charts when selecting bearings for any application. The right choice ensures optimal performance, longevity and safety of your machinery or system.
